Calculations In Visuals And Low Code Cells
Calculations allow you to perform more complex analyses than possible with the built-in functions available in the visual/low-code UI, without having to write a full SQL statement.
Calculations in Count are SQL expressions, written in a syntax that is heavily influenced by DuckDB (itself similar to PostgreSQL). They can be used with all databases supported by Count and — depending on the database — are parsed and transliterated to the appropriate dialect as required.
Getting started
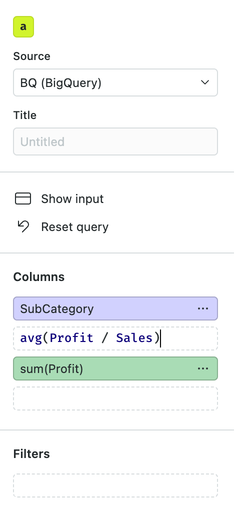
You can apply calculations to selects, filters and join constraints in visuals and low-code cells. In order to add or edit a calculation, either:
• Double click on a drop target or select to get an inline-editor
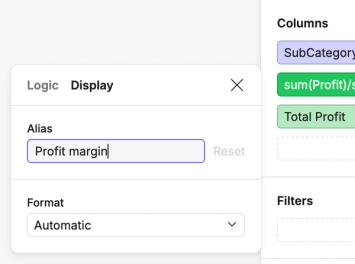
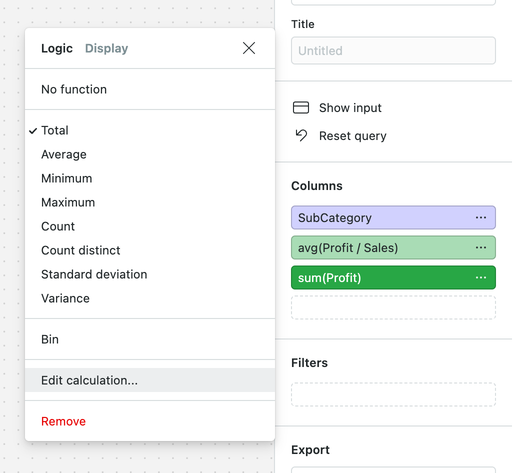
• Click on a select, filter or join constraint and select Edit calculation... to bring up the calculation modal
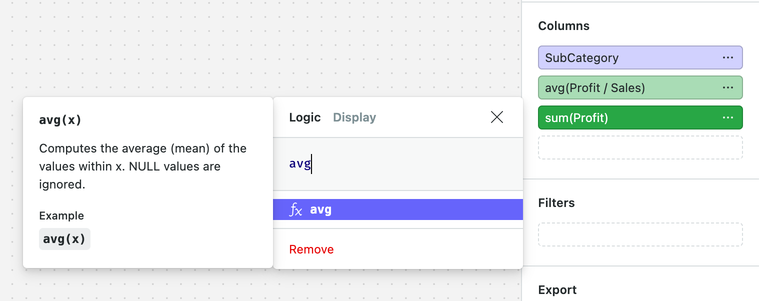
Once you're happy with your calculation, submit it using Shift + Enter.
Expressions
Calculations in Count support the following expression types:
• Literal (0, 0.123, 'abc', NULL, TRUE, FALSE)
• Identifier (Sales, Orders.Sales)
• Function (sum(Sales))
• Between (Sales BETWEEN 10 and 20)
• In (Region IN ('East', 'West'))
• Case (CASE WHEN Region = 'East' THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)
• Cast (CAST(Sales AS VARCHAR))
• Binary (2 + 2, A OR B)
• Unary (-2, NOT TRUE)
There's no explicit limit to the length of calculations.
Operators
The precedence of operators (the order in which expressions are evaluated) follows that of PostgreSQL. Parentheses can be used to override this.
| Precedence | Symbols | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | Unary minus | -1 |
| 2 | ^, ** | Exponentiation | 7 ^ 2 |
| 3 | *, /, % | Multiplication, Divison, Modulo | 7 * 2 |
| 4 | +, - | Addition, Subtraction | 7 + 2 |
| 5 | =, !=, <>, <, >, <=, >= | Comparison | 2 = 3 |
| 6 | IS | Is | X IS NULL |
| 7 | NOT | Logical negation | NOT TRUE |
| 8 | AND | Logical AND | A AND B |
| 9 | OR | Logical OR | A OR B |
Types
The following data types can be used in CAST expressions:
• VARCHAR ('abc')
• DOUBLE (1.23)
• INTEGER (123)
• DATE (DATE '2024-01-01')
• TIMESTAMP (TIMESTAMP '2024-01-01T00:00:00')
• TIMESTAMPTZ (TIMESTAMPTZ '2024-01-01T00:00:00Z')
• BOOLEAN (TRUE)
Functions
Count supports the following functions (note that some functions may be unavailable on some databases):
Text
| Function | Description | Example | Result | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CONCAT(string, ...) | Concatenate any number of strings together. | CONCAT('Hello', ' ', 'World') | 'Hello World' | All |
CONTAINS(string, substring) | Returns true if string contains substring. | CONTAINS('abc', 'c') | true | All |
ENDS_WITH(string, substring) | Returns true if string ends with substring. | ENDS_WITH('abc', 'c') | true | All |
LEFT(string, length) | Extracts the left-most characters from the string. | LEFT('Hello World', 2) | 'He' | All |
LENGTH(string) | Number of characters in the string. | LENGTH('Hello World') | 11 | All |
LOWER(string) | Converts string to lower case. | LOWER('Hello') | 'hello' | All |
LPAD(string, count, pad?) | Pads the string with the character from the left until it has count characters. | LPAD('Hello', 10, '<') | '<<<<<Hello' | All |
LTRIM(string) | Removes leading spaces from the string. | LTRIM(' Hello') | 'Hello' | All |
REPEAT(string, count) | Returns the original string repeated count times. | REPEAT('abc', 2) | 'abcabc' | All |
REPLACE(string, source, target) | Replaces any occurrences of the source with target in string. | REPLACE('Hello World', 'World', 'Universe') | 'Hello Universe' | All |
REVERSE(string) | Reverses the string. | REVERSE('Hello') | 'olleH' | All |
RIGHT(string, count) | Extracts the right-most count characters from the string. | RIGHT('Hello World', 2) | 'ld' | All |
RPAD(string, length, pad?) | Returns the original string with trailing spaces added up to length characters. | RPAD('Hello', 10, '<') | 'Hello<<<<<' | All |
RTRIM(string) | Removes trailing spaces from the string. | RTRIM('Hello ') | 'Hello' | All |
SPLIT_PART(string, delimiter, position) | Split the string along the delimiter and return the data at the (1-based) index of the list. If the index is outside the bounds of the list, returns an empty string. | SPLIT_PART('a|b|c', '|', 2) | b | Athena, BigQuery, Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Redshift, Snowflake |
STARTS_WITH(string, substring) | Returns true string begins with substring. | STARTS_WITH('abc', 'a') | true | All |
STRPOS(string, substring) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of substring. Returns 0 if the substring is not found. | STRPOS('Hello World', 'World') | 7 | All |
SUBSTRING(string, position, length) | Extract a substring of length characters from character position. | SUBSTRING('Hello', 2, 2) | 'el' | All |
TRIM(string) | Removes whitespace from both sides of the string. | TRIM(' Hello World ') | 'Hello World' | All |
UPPER(string) | Converts the string to upper case. | UPPER('Hello World') | 'HELLO WORLD' | All |
Numeric
| Function | Description | Example | Result | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ABS(x) | Computes the absolute value of x. | ABS(-1) | 1 | All |
ACOS(x) | Computes the arc cosine of x. | ACOS(0) | 1.5707963268 | All |
ASIN(x) | Computes the arc sine of x. | ASIN(0) | 0 | All |
ATAN(x) | Computes the arc tangent of x. | ATAN(0) | 0 | All |
ATAN2(x, y) | Computes the arc tangent of x and y. | ATAN2(0, 1) | 0 | All |
CEIL(x) | Computes the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to x. | CEIL(1.5) | 2 | All |
COS(x) | Computes the cosine of x. | COS(0) | 1 | All |
DEGREES(x) | Computes the degrees of x. | DEGREES(PI() / 2) | 90 | All |
DIV(x, y) | Returns the result of integer division of x by y. | DIV(5, 2) | 2 | All |
EXP(x) | Computes the exponential of x. | EXP(1) | 2.718281828459045 | All |
FLOOR(x) | Computes the largest integer value that is less than or equal to x. | FLOOR(1.5) | 1 | All |
LN(x) | Computes the natural logarithm of x. | LN(100) | 4.605170185988092 | All |
LOG(x, y) | Computes the logarithm of x to base y. | LOG(100, 10) | 2 | All |
LOG10(x) | Computes the logarithm base 10 of x. | LOG10(100) | 2 | All |
MOD(x, y) | Computes the modulo of x and y. | MOD(5, 2) | 1 | All |
PI() | Returns the value of π. | PI() | 3.141592653589793 | All |
POWER(x, y) | Computes the value of x raised to the power of y. | POWER(2, 3) | 8 | All |
RADIANS(x) | Computes the radians of x. | RADIANS(90) | 1.570796326 | All |
RANDOM() | Returns a random real number between 0 and 1. | RANDOM() | various | All |
ROUND(x, precision) | Rounds x to precision. | ROUND(1.23456, 2) | 1.23 | All |
SIGN(x) | Computes the sign of x. | SIGN(-17) | -1 | All |
SIN(x) | Computes the sine of x. | SIN(0.5) | 0.4794255386 | All |
SQRT(x) | Computes the square-root of x. | SQRT(4) | 2 | All |
TAN(x) | Computes the tangent of x. | TAN(0.5) | 0.5463024898 | All |
TRUNC(x, precision) | Truncates x to precision. | TRUNC(1.23456, 2) | 1.23 | Athena, BigQuery, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Redshift, Snowflake |
Date
| Function | Description | Example | Result | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DATE_ADD(date, interval) | Adds an interval to a date. | DATE_ADD(DATE '2024-01-01', INTERVAL 2 YEAR) | 2026-01-01 | All |
DATE_SUB(part, start_date, end_date) | Returns the number of complete partitions between start_date and end_date. | DATE_SUB('year', DATE '2024-01-01', DATE '2026-01-01') | 2 | Athena, BigQuery, Databricks, DuckDB, MySQL, Snowflake, SQL Server, Synapse |
DATE_TRUNC(part, date) | Truncates a date to specified precision. | DATE_TRUNC('year', DATE '2024-07-06') | 2024-01-01 | All |
NOW() | Returns the current timestamp. | NOW() | Various | All |
TODAY() | Returns the current date. | TODAY() | Various | All |
Intervals take the form of:
• INTERVAL x <date_part>
• INTERVAL 'x <date_part> y <date_part> z <date_part> ...'
and the following are valid date parts:
• YEAR, YR, Y, YEAR, YRS
• QUARTER, QUARTERS
• MONTH, MON, MONTHS, MONS
• WEEK
• DAY, DAYS, D
• HOUR, HR, HOURS, HRS, H
• MINUTES, MIN, MINUTES, MINS, M
• SECOND, SEC, SECONDS, SECS, S
• MILLISECONDS, MILLISECOND, MS, MSEC, MSECS, MSECOND, MSECONDS
• MICROSECONDS, MICROSECONDS, US, USEC, USECOND, USECONDS[^1]
Date part
| Function | Description | Example | Result | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DAYOFMONTH(date) | Returns the integer day of the month. | DAYOMONTH(DATE '2023-07-12') | 12 | All |
DAYOFWEEK(date) | Returns the integer day of the week (Sunday = 0, Saturday = 6). | DAYOFWEEK(DATE '2023-07-12') | 3 | All |
DAYOFYEAR(date) | Returns the integer day of the year. | DAYOFYEAR(DATE '2023-07-12') | 193 | All |
MONTH(date) | Returns the integer month of year (January = 1). | MONTH(DATE '2023-07-12') | 7 | All |
QUARTER(date) | Returns the integer quarter of year (January-March = 1). | QUARTER(DATE '2023-07-12') | 3 | All |
WEEK(date) | Returns the week number of year (starting with 1). | WEEK(DATE '2023-07-12') | 28 | All |
YEAR(date) | Returns the year. | YEAR(DATE '2023-07-12') | 2023 | All |
Aggregate
| Function | Description | Example | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|
AVG(x) | Computes the average (mean) of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | AVG(x) | All |
CORR(x, y) | Calculates the Pearson correlation coefficient of non-null pairs in the specified columns. | CORR(x, y) | Athena, BigQuery, Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Snowflake |
COUNT(arg) | Counts the number of non-null values in the specified column. If no column is specified, counts the number of rows in the table. | COUNT(x) | All |
COVAR_POP(x, y) | Calculates the population covariance of non-null pairs in the specified columns. | COVAR_POP(x, y) | Athena, BigQuery, Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Snowflake |
COVAR_SAMP(x, y) | Calculates the sample covariance of non-null pairs in the specified columns. | COVAR_SAMP(x, y) | Athena, BigQuery, Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Snowflake |
MAX(x) | Returns the maximum value of non-null expressions. | MAX(x) | All |
MEDIAN(x) | Computes the median of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | MEDIAN(x) | Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Redshift, Snowflake |
MIN(x) | Returns the minimum value of non-null expressions. | MIN(x) | All |
MODE(x) | Returns the most frequent value of non-null expressions. | MODE(x) | Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Snowflake |
QUANTILE_CONT(x, y) | Calculates the value of a continuous variable x at a specified percentile y, where y is between 0 and 1. The result is interpolated between adjacent values of x. | QUANTILE_CONT(x, 0.5) | Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Redshift, Snowflake |
QUANTILE_DISC(x, y) | Calculates the value of a discrete variable x at a specified percentile y, where y is between 0 and 1. The result is the value of x at the yth percentile. | QUANTILE_DISC(x, 0.5) | Databricks, DuckDB, PostgreSQL, Snowflake |
STDDEV_POP(x) | Computes the standard deviation of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | STDDEV_POP(x) | All |
STDDEV_SAMP(x) | Computes the standard deviation of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | STDDEV_SAMP(x) | All |
SUM(x) | Computes the sum of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | SUM(x) | All |
VAR_POP(x) | Computes the variance of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | VAR_POP(x) | All |
VAR_SAMP(x) | Computes the variance of the values within x. NULL values are ignored. | VAR_SAMP(x) | All |
Window
| Function | Description | Example | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|
CUME_DIST() | Evaluates the cumualative distribution: the number of partition rows preceding the current row / total partition rows. | CUME_DIST() | All |
DENSE_RANK() | Calculates the rank of the current row without gaps. | DENSE_RANK() | All |
FIRST_VALUE(expr) | Evaluates expr for the first row in the window frame. | FIRST_VALUE(x) | All |
LAG(expr, offset, default) | Returns the value of expr evaluated at the row that is offset rows before the current row within the window frame. If there is no such row, instead return default. If offset is omitted, it defaults to 1. If default is omitted, it defaults to NULL. | LAG(x, 1, 0) | All |
LAST_VALUE(expr) | Evaluates expr for the last row in the window frame. | LAST_VALUE(x) | All |
LEAD(expr, offset, default) | Returns the value of expr evaluated at the row that is offset rows after the current row within the window frame. If there is no such row, instead return default. If offset is omitted, it defaults to 1. If default is omitted, it defaults to NULL. | LEAD(x, 1, 0) | All |
NTH_VALUE(expr, nth) | Evaluates expr at the nth row of the window frame. | NTH_VALUE(x, 2) | All |
NTILE(num_buckets) | Distributes the rows in an ordered partition into a specified number of groups, ranging from 1 to num_buckets. | NTILE(4) | All |
PERCENT_RANK() | Evaluates the relative rank of the current row: (rank - 1) / (total partition rows - 1). | PERCENT_RANK() | All |
RANK() | Calculates the rank of the current row with gaps. Rows with equal values receive the same rank value. | RANK() | All |
ROW_NUMBER() | Returns the number of the current row within the partition, 1-indexed. | ROW_NUMBER() | All |
Utility
| Function | Description | Example | Result | Supported databases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
COALESCE(x, ...) | Returns the value of the first non-null expression. All expressions must be of the same type. | COALESCE(NULL, 1, 2) | 1 | All |
GREATEST(x, ...) | Returns the greatest value of the list of expressions. All expressions must be of the same type. | GREATEST(1, 2, 3) | 3 | All |
IF(x, y, z) | If x is true, returns y, Otherwise, returns z. | IF(2 > 1, 'a', 'b') | 'a' | All |
IFNULL(x, y) | If x is null, returns y. Otherwise, returns x. | IFNULL(NULL, 1) | 1 | All |
LEAST(x, ...) | Returns the least value of the list of expressions. All expressions must be of the same type. | LEAST(1, 2, 3) | 1 | All |
NULLIF(x, y) | Returns null if x = y, otherwise returns x. | NULLIF(1, 1) | NULL | All |
[^1]: